Physics
The integration of physics in our project involves the application of sound wave detection, signal processing, and energy conversion principles, enabling the device to replicate the auditory functions of the human ear. This approach combines acoustic mechanics, electromagnetic signal handling, and circuit dynamics to restore hearing functionality.
Integration
Electric Circuits and Amplification
-
Ohm's Law and the principles of amplification are essential for ensuring the captured sound signals are at a sufficient voltage/current level to be processed and transmitted clearly.
Energy Conversion
-
The system involves energy conversion, where sound energy is transformed into electrical energy, then back into sound energy for auditory perception.
Electric Circuits and Amplification
-
Concept: When electrical signals are processed in the implant, Ohm’s Law ensures that the current through the circuits is regulated correctly to prevent damage to components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors in the signal amplification stage.
-
Application: In signal amplification, voltage gain and current control are essential. Using Ohm's Law, you can calculate the proper resistance values to set the gain in amplifiers and avoid excessive current draw that might damage components or reduce battery life.
Vout = Vin × R2
R1 + R2
where:
-
VoutVout = output voltage to the next component,
-
R1, R2 = resistors in the voltage divider.
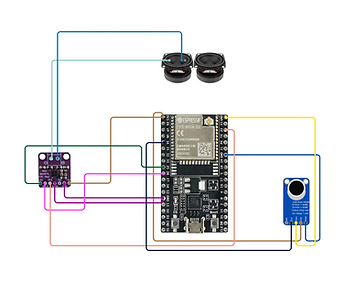

Electric Circuits and Amplification
-
Concept: The microphone (MAX9814) is responsible for capturing sound and converting it into an electrical signal. Energy conservation in the microphone is essential to ensure that the implant works efficiently, especially since it operates continuously in real-time.
-
Physics Principle: Active power management techniques can be used to ensure that the microphone only consumes power when necessary (e.g., when sound is detected). Power is consumed both by the microphone's internal circuitry and by the amplification stage.
-
Application: The MAX9814 is designed with automatic gain control (AGC), which adjusts the amplification based on the detected sound level. This helps prevent the microphone from amplifying low-level sounds unnecessarily, conserving power.
-
Formula for Power Consumption: The power consumed by the microphone can be calculated as:
P=V×IP=V×I
where: -
PP = power consumed by the microphone,
-
VV = supply voltage (typically 3.3V for the MAX9814),
-
II = current consumed (in milliamps).
